Antibiotic Resistance and your Health |
| In Module 2 - Lab Exercise, you observed how antibiotic resistance genes can move between bacteria by conjugation. Learn here how this kind of gene transfer affects you own health! |
The lifestyle of bacteria allows them to quickly select for any trait necessary for survival, including antibiotic resistance. If bacteria are challenged with an antibiotic and one cell in the population acquires resistance, it will flourish while the other cells are killed off.
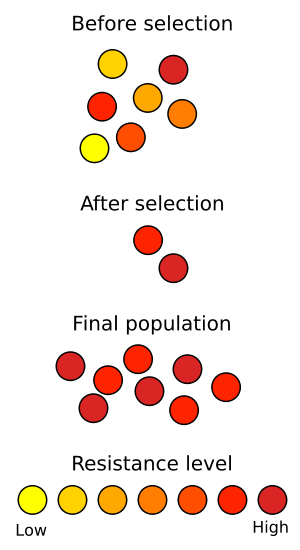
| Schematic representation of how antibiotic resistance evolves via natural selection. |
Source: Wikipedia (link to diagram) |
The top section represents a population of bacteria before exposure to an antibiotic.
The middle section shows the population directly after exposure, the phase in which selection took place.
The last section shows the distribution of resistance in a new generation of bacteria.
The legend indicates the resistance levels of individuals.
|
Antibiotics are a precious resource in our fight against bacterial pathogens, but as you observed in the Module 2 - Lab Exercise, resistance can easily develop in bacteria. Our actions can help determine whether future generations will have antibiotics available to combat both diseases that we are currently exposed to as well as new ones that may arise.
Questions to think about:
1. Do all illnesses benefit from antibiotic treatment?
2. How bad is the problem of antibiotic resistance?
3.
How do microbes overcome antibiotics?
Answers to these questions and much more can be found at:
Why Files website
Microbe World - Antibiotic Resistance resources
Get Smart: Know When Antibiotics Work from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention
